What Is UPC Barcode? Everything You Need to Know
Updated on September 22, 2025, by Xcitium
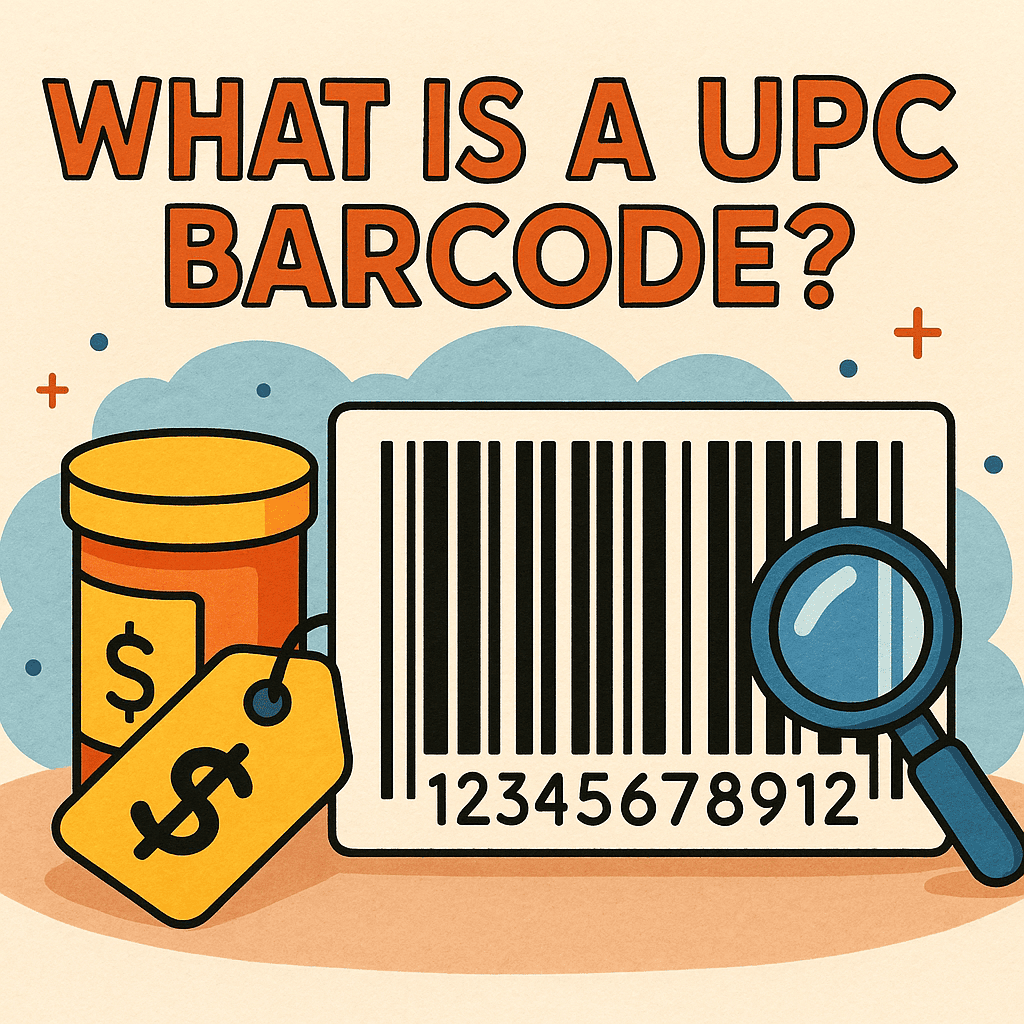
Have you ever picked up a product and noticed the black-and-white striped code on its packaging, then wondered, “What is UPC barcode and why is it so important?” UPC barcodes are everywhere—in supermarkets, warehouses, and online stores. For businesses and IT leaders, these codes aren’t just about tracking products; they’re about efficiency, data accuracy, and security.
In this article, we’ll break down what a UPC barcode is, how it works, why it matters in business and cybersecurity, and how enterprises can optimize their use for security and scalability.
What Is UPC Barcode?
A UPC barcode (Universal Product Code) is a machine-readable symbol used worldwide to identify and track products.
- Format: It typically contains 12 numeric digits.
- Components: Divided into sections for manufacturer ID, product ID, and a check digit.
- Purpose: Ensures products can be scanned quickly at checkout or tracked across supply chains.
👉 In simple terms, a UPC barcode is like a digital fingerprint for products.
How Does a UPC Barcode Work?
To fully answer what is UPC barcode, you need to understand how it functions.
- Scanning: A barcode scanner reads the black-and-white lines.
- Decoding: The scanner converts these lines into numbers.
- Database Match: The numbers link to product information stored in a database.
- Action: Systems retrieve details like price, stock level, or origin.
👉 UPC barcodes streamline operations by replacing manual entry with fast, error-free scanning.
Components of a UPC Barcode
When you ask, what is UPC barcode made of?—here’s the breakdown:
- Number System Digit: Identifies product type (e.g., food, drug, coupon).
- Manufacturer Code: Unique identifier for the brand.
- Product Code: Specifies the exact product.
- Check Digit: Ensures accuracy during scanning.
Types of UPC Barcodes
UPC barcodes aren’t one-size-fits-all.
- UPC-A: Standard 12-digit format used in most retail.
- UPC-E: Compressed version for smaller packages.
- EAN (European Article Number): Similar to UPC, used internationally.
👉 Choosing the right type depends on market, packaging, and compliance needs.
Business Benefits of UPC Barcodes
For IT managers, CEOs, and cybersecurity leaders, knowing what is UPC barcode also means understanding its advantages.
- Efficiency: Faster checkouts and inventory management.
- Accuracy: Reduces human error in data entry.
- Cost Savings: Streamlines supply chain operations.
- Analytics: Provides real-time data on sales trends.
- Scalability: Supports enterprise growth with standardized tracking.
UPC Barcode Security Considerations
While UPC barcodes seem harmless, they also pose cybersecurity risks.
- Counterfeit Products: Fake barcodes can mislead consumers and businesses.
- Data Manipulation: Malicious actors could tamper with barcode databases.
- Phishing & Fraud: Hackers can use lookalike codes in scams.
- Inventory Theft: Weak tracking can hide fraudulent product movements.
Security Best Practices
- Integrate barcode scanning with secure databases.
- Regularly audit inventory systems.
- Use cryptographic barcode solutions for sensitive industries.
- Educate staff on barcode tampering risks.
UPC Barcode vs. QR Code
Executives often ask: what is UPC barcode compared to QR code?
- UPC Barcode: Holds numeric data only, mostly for product identification.
- QR Code: Stores larger amounts of information, including links and text.
- Business Use: UPC dominates retail, while QR is versatile in marketing and payments.
👉 Many enterprises use both technologies depending on the use case.
Real-World Applications of UPC Barcodes
- Retail: Price lookup and checkout.
- Warehousing: Inventory tracking and restocking.
- Healthcare: Medical supplies and drug tracking.
- Cybersecurity: Monitoring supply chains for vulnerabilities.
Common Problems with UPC Barcodes
Even though UPC is reliable, IT teams may face challenges:
- Unreadable Barcodes: Due to damage or poor printing.
- Database Mismatch: Incorrect product data linked to the code.
- Standard Confusion: Using UPC vs. EAN in global operations.
- Scalability Issues: Outgrowing assigned manufacturer codes.
FAQs on UPC Barcodes
Q1. What is UPC barcode used for?
It’s used for product identification, pricing, and inventory management.
Q2. Are UPC barcodes unique worldwide?
Yes, each UPC is tied to a unique product through GS1 standards.
Q3. Can UPC barcodes be faked?
Yes, counterfeiters can copy them, which is why database validation is critical.
Q4. What’s the difference between UPC and SKU?
UPC is standardized across industries, while SKU is internal to each business.
Q5. Do UPC barcodes expire?
No, once issued, they remain valid unless reassigned by the manufacturer.
Conclusion: Why UPC Barcodes Still Matter
So, what is UPC barcode? It’s a universal product identifier that streamlines business processes, reduces errors, and provides valuable data for enterprises. But in today’s cyber-driven world, UPC codes must be secured and integrated with advanced IT systems to prevent misuse.
For IT managers, cybersecurity leaders, and executives, UPC barcodes represent more than retail tools—they’re part of a data ecosystem that requires protection.
👉 Looking to safeguard your supply chain and enterprise systems? Learn how Xcitium’s Zero-Trust solutions can protect your business from hidden risks.