Protect Network Endpoints
with Patented Auto Containment
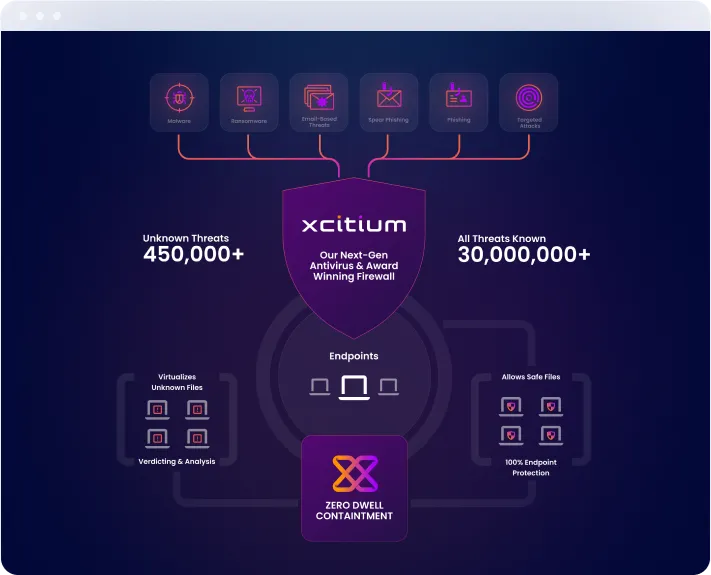
Protect your entire network with Xcitium’s patented Auto Containment technology, which ensures that any unknown or potentially malicious files are automatically contained before they can execute and cause harm. By securing every endpoint across your network, Xcitium provides an unparalleled defense that stops threats in their tracks, keeping your critical data and systems safe from even the most sophisticated cyberattacks.
Request DemoKey Features
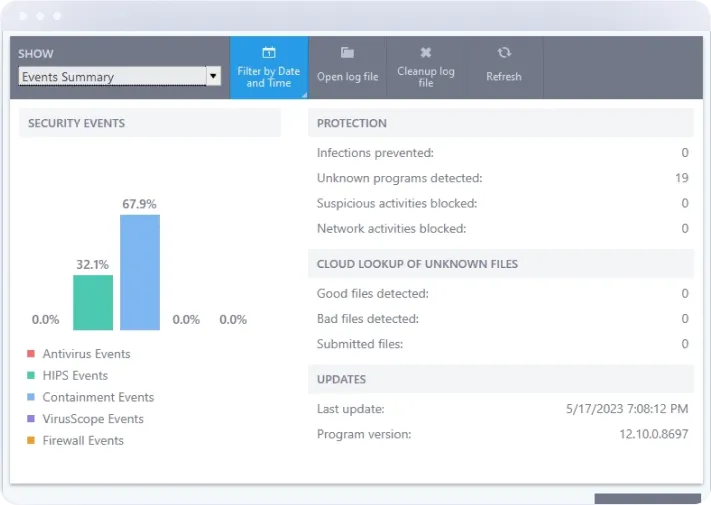
Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS)
Our advanced IDPS continuously monitors network traffic for suspicious activity, identifying and blocking potential threats in real-time. With sophisticated algorithms and machine learning capabilities, Xcitium's IDPS can detect both known and unknown threats, providing a proactive defense against cyber attacks.
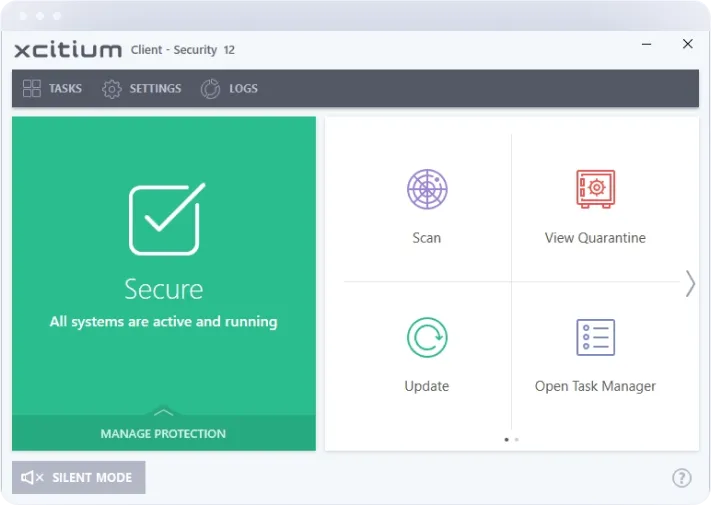
Next-Generation Firewall
Xcitium’s NGFW combines traditional firewall protection with advanced security features such as deep packet inspection, application-level filtering, and intrusion prevention. This comprehensive approach ensures that only legitimate traffic is allowed into your network, while malicious activities are swiftly blocked.
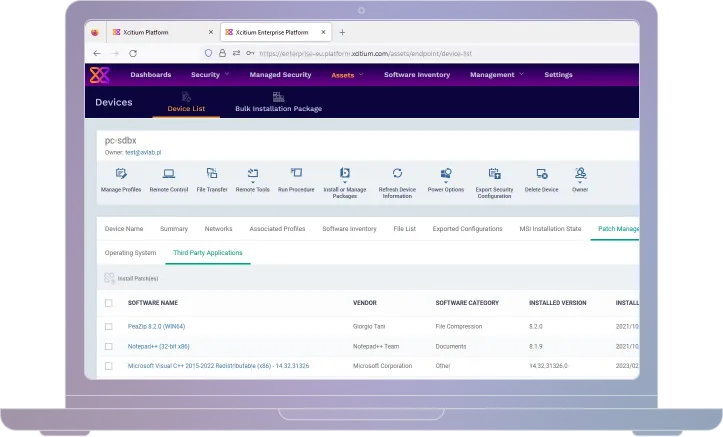
Secure Remote Access
Whether your team is working from the office or remotely, Xcitium ensures that every connection to your network is protected by advanced security protocols. With real-time monitoring and robust encryption, your IT administrators can remotely access and manage devices across your network with confidence.
Network Traffic Analysis
Gain deep insights into your network traffic with Xcitium’s network traffic analysis tools. Our platform provides detailed visibility into network activities, helping you identify patterns, detect anomalies, and respond to potential threats before they escalate.
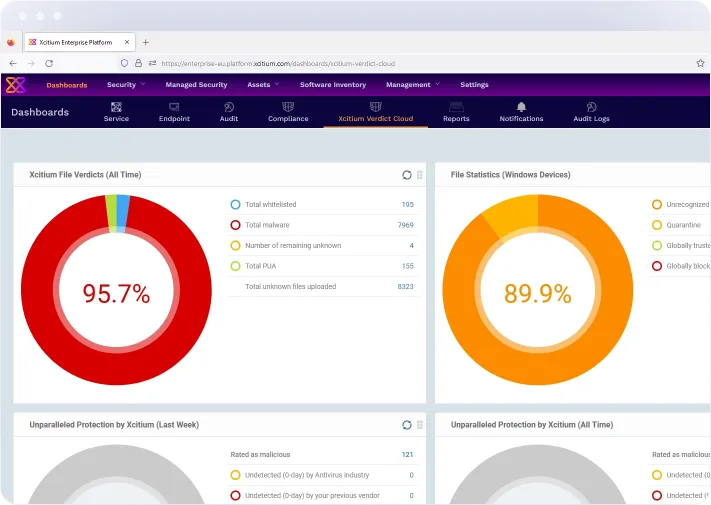
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Adopt a Zero Trust approach with Xcitium’s ZTNA. By verifying every user and device before granting access to your network, our platform ensures that only authorized entities can interact with your sensitive data and applications, minimizing the risk of internal and external threats.
Benefits
Integration

With years of experience in cybersecurity, Xcitium is a trusted leader in network security. Our solutions are backed by extensive research and development, ensuring they meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.

We provide 24/7 support to ensure your network remains secure at all times. Our team of experts is always available to assist you with any issues or concerns, providing peace of mind and uninterrupted protection.

At Xcitium, we are committed to staying ahead of the curve. Our dedicated research team continuously develops new technologies and updates our platform to address emerging threats, ensuring your network is always protected against the latest cyber risks.




