With increasing cyber threats, people struggle to keep their vital documents safe and secure. There are multiple types of cyberattacks available that can be harmful to your system, and ransomware is one of them.
You might wonder what it is and how ransomware allows hackers to do it. In this article, we will solve every query of yours, and here is something you must comprehend.
Ransomware allow hackers
In order to encrypt, delete, or exploit data, intellectual property, or Confidential information, pirates use malware. Cybercriminals use ransomware to hold information, devices, or systems, hostage until the victim pays the ransom, which is usually a secure, untraceable payment.
Cyberattack is one of the most profitable tactics for cybercriminals, with increasing ransom demands ranging from $1 million to USD 10 million.
You must know that even after you pay a ransom to the hackers, there is no guarantee that you will be able to restore your data on your system.

What is the ransomware hacker's technique?
There are two methods that ransomware allows hackers to persuade victims to pay money using two methods:
1. Data Encryption
A ransomware attack encrypts a victim's files in order to demand a ransom payment to decrypt them. The encrypted files vary from one ransomware variant to another, but they typically enter the system and search through specific file types. The ransomware variants that are available today come with self-spreading capabilities. It simply means that they are capable of infiltrating other machines within the network
2. Data Theft
For the ransomware hacker to profit, data encryption is not enough. You will notice that the victims of the cyber attacks are instructed not to make ransom payments. Reporting the attack to the authorities and accepting the losses is advised. Ransomware allows hackers to browse valuable and confidential documents or data from the infected device to send themselves a copy. They do this before encrypting the victim's data. Once they receive the data, they ask the victim to make ransom payments.
The amount of the payment is concluded as per the data stolen.
What are the types of ransomware?
Ransomware attacks come in different variants. Here, we will mention some of the most common types of ransomware attacks.
#Crypto ransomware or encryptors
It is one of the popular methods of attack. It is also referred to as data kidnapping, which is an effective and highly lucrative method. In this attack, the convict encrypts the unreadable data and then insists on a ransom for the keys to break it.
#Exfilteration or Leakware
Exfilteration or Leakware- Also known was doxware or leakware, this ransomware comes with high risks as it gives the authority to hackers to steal your sensitive data and threaten to release it to the public. The victims of this activity can bear severe consequences for their business. It also allow hackers to damage your public image as well as adversely affect your business, hence leading to fines for breaching the data protection regulations.
#Screen lockers
This is another type of ransomware attack. The screen locker is a type of malware that stops you from accessing a computer or machine until you disburse the ransom requested by the assaulter. When you attempt to log in to an infected computer, the screen locker displays a message requesting payment. It is often accompanied by a countdown time designed to scare the victim into paying before the ransom increases or they lose their files. In this form of attack, the risk is low. Ransomware allows hackers to ask for the ransom once they have encrypted the file.
#Scareware
In scareware, social engineering tactics are used to trick the user. Ransomware allows hackers to make users believe their computer has been infected with malware or has encountered some problem requiring urgent action. You will notice a pop-up alert that shows the logo of legitimate security software, instructing you to purchase and install software to resolve the issue. The risk is very low in this, and the software will do nothing more than remove the message, or it may contain malware designed to cause more severe harm.
How can you protect yourself from cyberattacks?
Multiple ways can help save your data from ransomware attacks. Here is something you ought to understand.
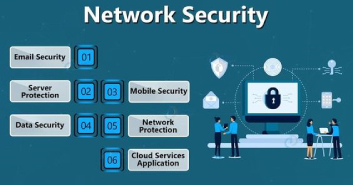
Email Security
One of the most common ways to secure your system is email security. Phishing is the most common delivery vector for ransomware, and it is an email security key that can scan and recognize ransomware in emails before they get to the target computer.
Mobile security
These days, mobile is used for both personal and professional use. Mobile security is critical to protect against ransomware because it gives freedom to hackers to use their cellphones to attack.
Network Security
Once attackers attack one device, they move through the network to find other targets. Keeping up with the network security standards is suggested as it helps blocking infections at the initial stage and inhibit the spread of ransomware.
Final Words
This is the complete information about what ransomware will enable hackers to do. It is one of the most risky cyberattacks that can ruin your data. It is necessary to take the measures required in order to keep these attacks at bay.
To learn more about ransomware attacks, you must visit the website below.