Cloud Security
Secure your entire cloud infrastructure with Xcitium’s Cloud Security solution. Designed to safeguard modern cloud-native environments, Xcitium CNAPP (Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform) and Cloud-Native Network Detection and Response deliver Zero Trust security that spans traditional and modern workloads, from virtual machines to Kubernetes clusters.
Free Cloud Security Assessment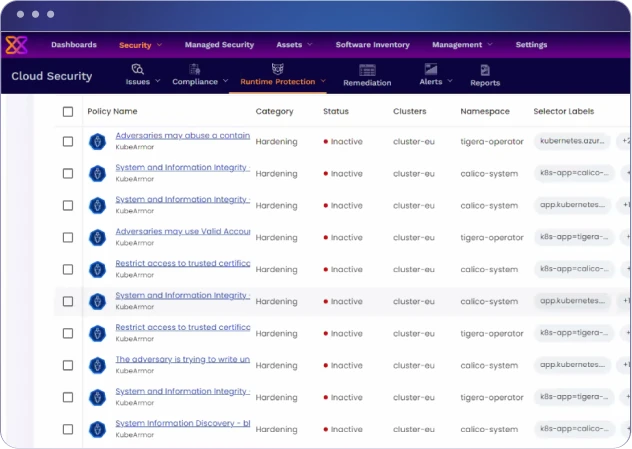
Key Features & Differentiators

Application Security Posture Management (ASPM)
- Analyzes source code for vulnerabilities without needing to run the application
- Stimulates attack scenarios on running app to identify weaknesses
- Evaluates third-party dependencies and libraries in open source
- Provides Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scans based on Terraform and Dockerfile
- Key Differentiators: Centralized view with extensive tools for SCA, SAST, DAST, and IAC; prioritizes vulnerabilities based on runtime exposure, exploitability, and environmental factors

Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
- Agentless scanning for continuous compliance.
- GRC Roadmap and adherence to security frameworks like CIS, HIPAA, PCI, SOC2, ISO27001.
- Monitors configuration drift and alerts on deltas.
- Key Differentiators: Continuous monitoring, 1-click remediation, configuration drift visibility, and customizable dashboards.

Comprehensive Security Suite
- Covers various security aspects including SPM, CSPM, KIEM, CWPP, and GRC
- Supports static, dynamic, and infrastructure security testing
- Enables multi-cloud security with continuous detection, response, and reporting
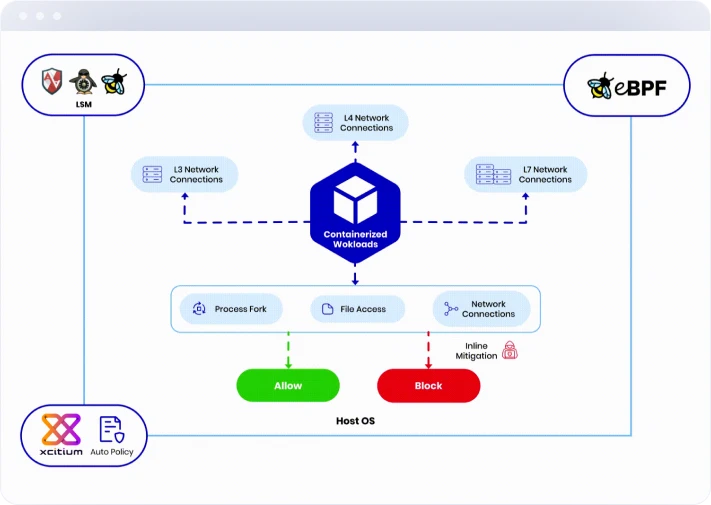
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
- Implements network segmentation and automatic Zero Trust policies
- Supports multi-cloud and multi-cluster environment.
- Key Differentiators: Automated policy generation and enforcement; inline mitigation recommendations for enterprise cloud workload protection

Kubernetes Identity & Entitlement Management (KIEM)
- Agentless scanning of Kubernetes identity misconfigurations
- Visualizes relationships between entities and resources using graph visualization
- Key Differentiators: Predefined critical queries for identifying principals with excessive privileges, service accounts without workloads, and more

Challenges of Modern Cloud Security
Xcitium is designed to address these modern challenges by providing a unified platform that not only enhances protection but also simplifies management across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Its focus on inline mitigation ensures that threats are neutralized before they can cause harm, setting it apart from other solutions that react only after an attack has occured.
Benefits
Efficiency

With years of experience in cybersecurity, Xcitium is a trusted leader in network security. Our solutions are backed by extensive research and development, ensuring they meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.

We provide 24/7 support to ensure your network remains secure at all times. Our team of experts is always available to assist you with any issues or concerns, providing peace of mind and uninterrupted protection.

At Xcitium, we are committed to staying ahead of the curve. Our dedicated research team continuously develops new technologies and updates our platform to address emerging threats, ensuring your network is always protected against the latest cyber risks.




