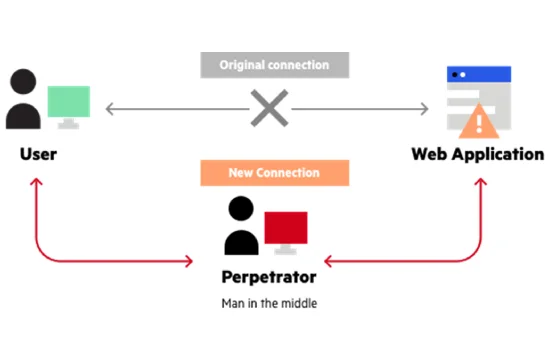
What is a Man in the Middle (MITM) Attack?
A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack is a type of cyberattack where an attacker secretly intercepts and alters communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other. This attack allows the hacker to eavesdrop on conversations, steal sensitive data, manipulate messages, or inject malicious content into the communication. MITM attacks are commonly used to steal login credentials, financial information, or personal details, making them a serious cybersecurity threat.
These attacks often occur in unsecured or weakly protected communication channels, such as public Wi-Fi networks, where attackers can position themselves between a user and the website or service they are accessing. When a user connects to an unprotected network, an attacker can use tools to intercept and modify traffic, allowing them to steal data or impersonate legitimate services.
One of the most common methods used in MITM attacks is Wi-Fi eavesdropping. Cybercriminals set up rogue access points that appear to be legitimate networks, tricking users into connecting. Once connected, the attacker can monitor all data transmitted between the victim’s device and the internet, capturing login credentials, emails, and even encrypted communications if they manage to downgrade security protocols.
Another common form of MITM attack is session hijacking, where an attacker takes over an active session between a user and a website. This often happens when attackers steal session cookies, which are small pieces of data stored on a user’s browser to maintain authentication. By obtaining these cookies, hackers can gain unauthorized access to a user’s account without needing login credentials.
DNS spoofing is another technique used in MITM attacks, where an attacker alters the Domain Name System (DNS) responses to redirect users to malicious websites. Instead of reaching the intended secure site, users unknowingly enter sensitive information on fraudulent pages controlled by hackers. This method is often used for phishing scams and credential theft.
MITM attacks can also involve SSL stripping, where attackers downgrade secure HTTPS connections to unencrypted HTTP connections, making it easier to intercept and manipulate data. Users may not even notice this downgrade, especially if they are not vigilant about checking for the padlock icon in the browser’s address bar.
To protect against MITM attacks, users and organizations should implement strong security measures such as using VPNs, enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA),and avoiding unsecured public Wi-Fi networks. Additionally, website owners should enforce HTTPS encryption and utilize secure protocols like TLS to safeguard data transmission. By staying informed about MITM attack techniques and prevention strategies, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to these cyber threats.
MITM Attack vs Other Cyber Threats
A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack is just one of many cyber threats that pose serious risks to individuals and businesses. While it shares some similarities with other forms of cyberattacks, it has distinct characteristics that set it apart. Understanding how MITM attacks compare to other threats such as phishing, malware, ransomware, and DDoS attacks can help organizations and individuals improve their cybersecurity posture.
One of the key differences between a MITM attack and other cyber threats is its method of execution. MITM attacks involve an attacker intercepting communication between two parties without their knowledge. Unlike phishing attacks, which rely on social engineering tactics to trick users into revealing sensitive information, MITM attackers actively position themselves between the victim and the intended recipient to manipulate or steal data in real-time. Phishing attacks typically use fake emails or websites to lure users into providing their credentials, whereas MITM attackers exploit vulnerabilities in network security to eavesdrop on legitimate communications.
Compared to malware and ransomware, MITM attacks do not necessarily require malicious software to be installed on a victim’s device. Malware infections often involve tricking users into downloading infected files or exploiting software vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to a system. Ransomware, a type of malware, encrypts a victim's files and demands payment in exchange for decryption. MITM attacks, on the other hand, can occur without the victim’s direct interaction, especially when attackers exploit unsecured Wi-Fi networks, weak encryption protocols, or vulnerabilities in communication channels.
Another difference is in the impact of MITM attacks versus Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. A DDoS attack aims to overwhelm a network, website, or server with a flood of traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users. The primary goal of a DDoS attack is disruption, rather than data theft or manipulation. In contrast, MITM attacks are more stealthy, focusing on intercepting or altering sensitive information rather than causing immediate system failure. Both types of attacks can be damaging, but their objectives and execution differ significantly.
MITM attacks also differ from credential stuffing and brute-force attacks, where cybercriminals use automated scripts to repeatedly attempt username and password combinations until they gain unauthorized access. While these attacks focus on exploiting weak or reused passwords, MITM attackers manipulate live communication channels to extract sensitive data in real time, making them harder to detect.
Although MITM attacks have unique characteristics, they can often be combined with other cyber threats to increase their effectiveness. For example, an attacker could use phishing to trick a victim into connecting to a malicious Wi-Fi hotspot, where a MITM attack is then used to intercept login credentials. Similarly, MITM techniques could be employed to inject malware into legitimate downloads, leading to further system compromise.
To defend against MITM attacks and other cyber threats, organizations must implement a multi-layered security strategy. This includes using strong encryption protocols, secure communication channels, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and endpoint security solutions. Individuals should also avoid using unsecured public Wi-Fi networks, verify website security with HTTPS, and be cautious of suspicious emails or network requests. By understanding how MITM attacks compare to other cyber threats, users can take proactive steps to protect their sensitive data and maintain a secure online presence.
How Organizations Can Protect Their Networks from MITM Attacks
Organizations face a growing threat from Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, which can compromise sensitive data, disrupt business operations, and lead to financial losses. To defend against these attacks, businesses must implement a multi-layered security approach that focuses on securing network infrastructure, encrypting communications, and educating employees on best security practices.
One of the most effective ways organizations can protect their networks from MITM attacks is by enforcing strong encryption protocols. Data transmitted over a network should always be encrypted to prevent attackers from intercepting and manipulating sensitive information. Secure protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) and HTTPS should be used for all web communications, while email encryption tools like PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) or S/MIME can help secure email exchanges. Companies should also ensure that Secure Shell (SSH) is used instead of unsecured remote access methods when managing servers.
Another crucial defense is securing Wi-Fi networks to prevent unauthorized access. Organizations should use WPA3 encryption for their wireless networks and disable outdated protocols like WEP and WPA that are vulnerable to attacks. Implementing network segmentation can also help minimize the impact of an attack by isolating critical systems from general user traffic. Businesses should enforce strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to add an additional layer of security for accessing sensitive data and systems.
Regular software updates and patch management are essential for reducing vulnerabilities that MITM attackers might exploit. Cybercriminals often take advantage of outdated software, unpatched operating systems, or misconfigured security settings to execute attacks. Organizations should implement an automated patch management system to ensure that security updates are applied promptly across all devices and network components.
Another critical step is the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), especially for employees who work remotely or frequently connect to public Wi-Fi networks. A VPN encrypts data traffic, making it much more difficult for attackers to intercept communications. Businesses should provide employees with a corporate VPN solution and enforce its use for accessing company resources remotely.
Organizations should also deploy Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) to monitor network traffic for signs of MITM attacks. These systems analyze patterns and detect anomalies, such as unexpected SSL/TLS certificate changes or unusual network activity, which could indicate an ongoing attack. Additionally, implementing certificate pinning can help prevent attackers from using fraudulent SSL certificates to intercept secure communications.
Employee training and cybersecurity awareness programs play a vital role in preventing MITM attacks. Many cyberattacks succeed due to human error, such as employees connecting to unsecured Wi-Fi networks or falling for phishing attempts that lead to credential theft. Organizations should conduct regular security training sessions to educate employees about safe browsing habits, recognizing fake Wi-Fi networks, and verifying website security by checking for HTTPS encryption and valid SSL certificates.
To further enhance security, businesses should implement Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), which operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." This model ensures that every access request is authenticated, authorized, and continuously monitored, reducing the chances of MITM attacks succeeding.
By combining strong encryption, secure authentication, network monitoring, employee training, and Zero Trust principles, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of MITM attacks and strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture. Investing in proactive security measures today can help businesses protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and prevent costly security breaches in the future.