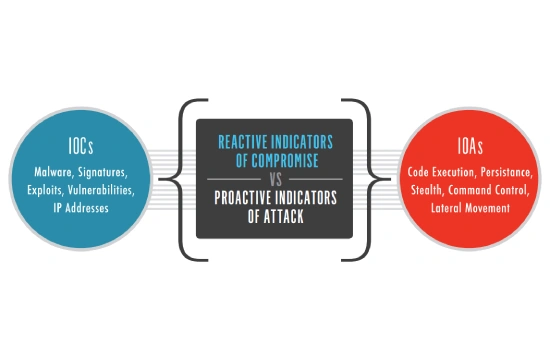
Key Differences Between IOA and IOC
Indicators of Attacks (IOA) and Indicators of Compromise (IOC) are both crucial in cybersecurity, but they serve distinct purposes in threat detection and response. IOA focuses on identifying malicious intent and behavior before an attack successfully breaches a system, while IOC is used to detect evidence of a security breach after it has already occurred. Understanding these differences is essential for organizations aiming to build a proactive cybersecurity defense strategy.
IOAs are proactive by nature, analyzing behavior patterns, tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers. Instead of relying on known signatures or artifacts left behind after an attack, IOAs detect threats based on intent. This means they look for activities such as unusual login attempts, privilege escalation, lateral movement, or suspicious file execution. By catching these actions early, security teams can stop an attack before it causes harm.
On the other hand, IOCs are reactive, as they are used to identify an attack that has already happened. They rely on forensic data, including IP addresses, file hashes, domain names, unusual outbound traffic, and other digital footprints left behind by cybercriminals. IOCs help organizations understand the scope of a breach, analyze the attacker’s methods, and implement corrective measures to prevent similar incidents in the future. However, since IOCs depend on historical data, they are less effective in preventing zero-day attacks or new, sophisticated threat techniques that have not yet been documented.
One of the key advantages of IOAs is their ability to detect unknown or evolving threats. Cybercriminals constantly change their attack methods to bypass traditional security measures. Because IOAs focus on behaviors rather than specific attack signatures, they provide better protection against emerging threats. Security solutions that incorporate IOAs, such as next-generation endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems, use machine learning and artificial intelligence to recognize suspicious patterns in real-time.
In contrast, IOCs are valuable for forensic analysis and incident response. After a breach occurs, security teams rely on IOCs to understand how attackers gained access, what data was compromised, and what vulnerabilities need to be addressed. This retrospective approach is essential for strengthening security postures and ensuring that similar attacks do not happen again. However, relying solely on IOCs can leave organizations vulnerable to initial attacks, as they do not provide real-time threat detection.
Both IOA and IOC play an important role in a layered cybersecurity approach. While IOAs help prevent attacks by detecting malicious intent, IOCs provide valuable insights after an attack to improve future defenses. Security teams should integrate both strategies to achieve a more comprehensive threat detection and response system. By leveraging real-time behavioral analysis through IOAs and forensic investigation through IOCs, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of successful cyberattacks while improving their ability to respond to incidents effectively.
To maximize security, companies should implement security tools that incorporate both IOA and IOC detection methods. Advanced security information and event management (SIEM) systems, threat intelligence platforms, and managed detection and response (MDR) services are examples of solutions that combine proactive and reactive threat detection techniques. By balancing prevention with post-incident analysis, organizations can create a resilient cybersecurity strategy capable of defending against today’s evolving cyber threats.
Why Both IOA and IOC Are Essential for Cybersecurity
In today's rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape, organizations must adopt a multi-layered defense strategy that includes both Indicators of Attacks (IOA) and Indicators of Compromise (IOC). While IOAs focus on detecting malicious intent before an attack is successful, IOCs help identify security breaches after they have occurred. Both play a critical role in cybersecurity, and integrating them into a unified threat detection and response strategy ensures a stronger and more resilient security posture.
IOAs are essential for proactive cybersecurity. They help security teams detect potential threats by analyzing behaviors and patterns that indicate an attack is in progress. Rather than waiting for an attack to leave a trail of evidence, IOAs focus on identifying suspicious activities such as unauthorized access attempts, privilege escalation, data exfiltration, and unusual file executions. This approach allows organizations to stop attacks before they can cause damage, reducing the risk of data breaches, ransomware infections, and system disruptions.
While IOAs provide early warning and prevention, IOCs are crucial for forensic analysis and incident response. Cybersecurity teams rely on IOCs to investigate past security incidents, understand attack methods, and implement countermeasures to prevent recurrence. IOCs include digital fingerprints such as malware signatures, malicious IP addresses, domain names, file hashes, and unusual network traffic patterns. By analyzing these indicators, organizations can determine the extent of a breach, assess the damage, and identify vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
One of the biggest challenges in cybersecurity is dealing with zero-day attacks and advanced persistent threats (APTs). Cybercriminals constantly evolve their tactics, making it difficult for traditional security tools to detect new threats based on known signatures alone. This is where IOAs become particularly valuable, as they focus on attacker behaviors rather than predefined attack patterns. However, even with strong IOA detection, some attacks may still succeed, making IOCs essential for post-incident investigation and remediation.
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy should not rely on just one approach. Using only IOAs without considering IOCs can leave gaps in historical analysis and forensic investigation, while relying solely on IOCs makes an organization reactive rather than proactive. Combining both ensures that security teams can detect, prevent, and respond to threats effectively. Organizations that integrate IOA and IOC detection methods through advanced security platforms—such as endpoint detection and response (EDR),security information and event management (SIEM),and managed detection and response (MDR) services—gain better visibility into threats and can act quickly to mitigate risks.
By leveraging both IOA and IOC, businesses can enhance their cybersecurity defenses, minimize downtime, and reduce financial and reputational damage caused by cyberattacks. The combination of proactive threat detection and reactive incident response provides a well-rounded security strategy, helping organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain robust protection against cyber adversaries.
Best Practices for Implementing IOA and IOC
Implementing Indicators of Attacks (IOA) and Indicators of Compromise (IOC) effectively requires a strategic approach that combines proactive threat detection with reactive incident response. By integrating both methodologies into a cybersecurity framework, organizations can strengthen their defenses against evolving threats while ensuring they can quickly identify and mitigate security incidents. Below are the best practices for implementing IOA and IOC in a way that enhances overall cybersecurity resilience.
The first step in implementing IOA and IOC is leveraging advanced security tools that support both real-time monitoring and historical analysis. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) platforms, and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions provide visibility into network activity and detect behavioral anomalies associated with attacks. These tools can correlate IOAs with IOCs, helping security teams identify threats early while also enabling post-incident investigations.
Threat intelligence plays a crucial role in strengthening IOA and IOC implementation. Organizations should subscribe to reputable threat intelligence feeds that provide up-to-date information on emerging attack techniques, malware signatures, and known threat actors. By incorporating this intelligence into security workflows, businesses can improve their ability to detect and respond to new threats effectively. Automated threat intelligence platforms help streamline the process by integrating this data into existing security tools.
Another key best practice is establishing robust behavioral analysis capabilities. Since IOAs focus on detecting attack patterns and behaviors rather than relying on known signatures, organizations should invest in machine learning-driven security analytics. AI-powered threat detection can identify suspicious activity such as unauthorized access attempts, unusual file movements, privilege escalations, and lateral movement within the network. By continuously monitoring for these behavioral indicators, security teams can detect attacks before they result in a breach.
Incident response planning is equally important when implementing IOC-based detection. Organizations should have well-documented incident response protocols that outline steps to take when an IOC is detected. This includes isolating compromised systems, conducting forensic analysis, identifying root causes, and applying remediation measures to prevent future incidents. Security teams should regularly update and test their incident response plans to ensure they remain effective against evolving threats.
Integrating IOA and IOC detection into a Security Operations Center (SOC) enhances real-time monitoring and response capabilities. A SOC staffed with cybersecurity analysts and threat hunters can continuously monitor security events, analyze behavioral anomalies, and correlate attack patterns with known compromise indicators. Security automation and orchestration can further improve efficiency by reducing manual intervention in threat detection and response processes.
Continuous training and awareness are also essential. Cybersecurity teams should receive regular training on the latest attack techniques, detection methodologies, and best practices for analyzing IOA and IOC data. Security awareness programs should also extend to employees, educating them on recognizing phishing attempts, suspicious emails, and other tactics used by cybercriminals to gain access to corporate networks.
Regular security assessments and penetration testing help validate the effectiveness of IOA and IOC detection mechanisms. Organizations should conduct routine vulnerability assessments, red team exercises, and simulated attack scenarios to identify gaps in their security posture. By testing how well security defenses can detect and respond to both known and unknown threats, businesses can refine their cybersecurity strategies and improve overall resilience.
Finally, organizations should adopt a Zero Trust security model that assumes no entity—whether internal or external—should be inherently trusted. Zero Trust principles enforce strict identity verification, least privilege access, and continuous monitoring of user and device behavior. This approach aligns well with IOA-based detection by focusing on intent and suspicious activity rather than solely relying on signature-based detection methods.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can maximize the effectiveness of IOA and IOC detection, reducing the risk of cyberattacks while ensuring rapid incident response and recovery. A well-integrated approach combining proactive and reactive security measures is key to maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture in an increasingly complex threat landscape.